2.1 Applying the 7-S framework to capacity building
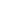
FIGURE 6:
OPERATIONAL FOCUS OF JAWUN’S PARTNERS
$
Health
9%
Safe
communities
19%
Governance
and reform
31%
Home
environment
2%
BA C
Early
childhood
1%
Economic
participation
14%
Education
and training
14%
Key focus
areas of Jawun’s
Indigenous partner
organisations
NOTE: CATEGORIES ARE TAKEN FROM THE COUNCIL OF AUSTRALIAN GOVERNMENTS ‘BUILDING BLOCKS’ FOR CLOSING THE GAP ON
INDIGENOUS DISADVANTAGE—SEE
WWW.HEALTHINFONET.ECU.EDU.AU/CLOSING-THE-GAP/KEY-FACTS/WHAT-ARE-THE-BUILDING-BLOCKS- AND-HOW-DO-THEY-FIT-IN.Each secondee works on a specific project brief,
and builds capacity in some form. In its impact
evaluation of Jawun, KPMG sought to define
the different ways secondees build capacity of
Indigenous organisations. It adapted a McKinsey
capacity assessment framework designed to guide
organisational effectiveness, known as the ‘7-S’
framework—strategy, structure, systems, shared
culture, staffing, style and skills (Figure 7)
. 20This
section uses the principles of that framework to give
a range of examples of Jawun secondments that
show capacity building in practice.
It’s one thing to have the leadership and the vision, but if you
don’t have the engine with strong capabilities in it, then you
don’t achieve the vision.
—NOEL PEARSON,
JAWUN PATRON AND FOUNDER OF CAPE YORK PARTNERSHIPS
2. STRENGTHENING INDIGENOUS ORGANISATIONS 25